Notes on the first homework assignment on the scientific fields of Astronomy,
Paleontology, Anthropology, and *Paleopathology.
(*The reading in paleontology follows below and sheds light on issues within the history of Homosapiens
over the last 100,000 years through the agricultural revolution)
 |
The image on the left is an artist's depiction of the so-called "big bang," the earliest verifyable event in history using scientific tools of the field of Astronomy. And like scientists in other fields, Astronomers don't ask questions like "Who or what created the 'big bang'?" Scientists are more interested in the processes of what we can see and verify through math and of course telescopes. Beyond the "big bang" event of creation, 13.7 billion years ago, Astronomers verify nothing. Religious and philosophical questions that go beyond the processes of how things occurred and continue to occure, are valid questions in their own right, but are different from science. Theologians, philosophers, and historians can still use scientific perspectives to gain insight into many questions and we will try to organize some of the major findings of various fields of science -- from Astronomy to Geology and Paleontology -- to have more lenses to explore possible answers to questions that can sometimes have multiple answers, depending on what lense you use. How might the tools of modern astronomy like high powered, sattelite-mounted infared telescopes, have affected the ancient Hebrews' creation story if they had had them availble then? Scientific discoveries have been a long time coming and it is worth reviewing the story of how our view of the world in space has changed over time. |
| You may want to pause while you are viewing the lecture, and draw a timeline of important events over the last two thousand years that you see as crucial to understanding the changing view of the universe. You might want to include the "turning-points" and "sticking-points" over time for the Christian church, regarding discoveries in Astronomy? |
Timeline notes from the lecture: The church supported Ptolemy (90-168CE) -- Greek earth-centric (geo-centric) over Aristarchus 310-230 B.C.E. helio-cetric (sun-based) view of the universe because it corresponded with the churches portrayal of the heavenly (celestial) spheres surrounding the earth, the City of God. Ptolomy's view was easy to verify by human experience (the earth stays still and everything else moves around it), and it supported the church's view of the earth as central (imperfect) to the perfect, celestial spheres above it. A thousand years later (16th century) the beginning of the Scientific Revolution, people like Francis Bacon demanded evidence for assumtions that the church had made for over a thousand years. A split between people relying on authority and people needing verifyable evidence proceeded. in the 16th century, hence, a Scientific Revolution. --> 11:00 Copernicus (1473-1543) found many unexplainable problems the eath-centered view of the planets (retrograde movement, in particular), disappeared with a sun-centered view of the solar system. Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) used careful (naked-eye) observation and mathematics to uncover further evidence, especially regarding comets and their apparent movement through the heavenly (crystaline) spheres. --> 12:30 Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) discovered through math that the planets did not surround the sun in perfect circles but in elipses. 13:00 Galelio Galilei (1564-1642) was one of the first to use a telescope to show that the sun was not perfect and had spots on it that were visible from time to time. Isaac Newton (1642-1727) eventually added it all together and argued that the earth was subject to the same forces as the rest of the visible universe. In his Principia Mathematica (1687) he argued that there was a gravitational principal based on the mass of an object . The new Cosmology that came from the Scientific Revolution in the 17th century included the posibility that the universe was infinite. For several centuries, however, there were too many contradictions to the infinite universe thesis. Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) worked in the 1920s to prove that the universe is expanding through evidence of the "red shift." Henrietta Leavitt (1868-1921) built on the work of other 19th century astronomers who used parallax (high school trigonometry to begin to figure out the distances between earth and stars -- the position and motion of stars). Telescopes and long-term observations were required in the 19th century to begin to map the universe. Leavitt discovered Cepheid variables, based on light pulse patterns in the stars in the constellation, Cepheus. She proposed that because size/mass and brightness correspond, you could calculate the distance of these distant stars.Hubble built on such Cepheid variables to find other "Cepheids," or the pulsing light of dying stars, to map the distances between stars in other galaxies.
Human history is so brief in the Astronomer's 13.7 billion year scale of time, that we see almost no pattern at all, unless we include the story of human life with the story of the rest of life on planet earth. For example, since our life on land is dependent on the protection that the ozone layer gives us from the most harmful rays of the sun, we have to see what life forces helped to create the ozone layer, and the astronomers timeline does provide clues. How many billions of years did it take to for cynobacteria and algae to form excesses of oxygen that helped creat the ozone layer and enable the "Cambrian Explosion" of life forms and populations on earth? How long has sexual reproduction of life on earth has been around, and what does that say about it and life on earth? Are there any other clues to the mysteries of human existence in the universe using the scale of the universe? What is the predominant forms of life on earth that have stood the harshest tests of time? What lessons do we have to learn from other life forms and the planet in general, using the astronomers lens?
Discerning patterns using the lens of an Astronomy
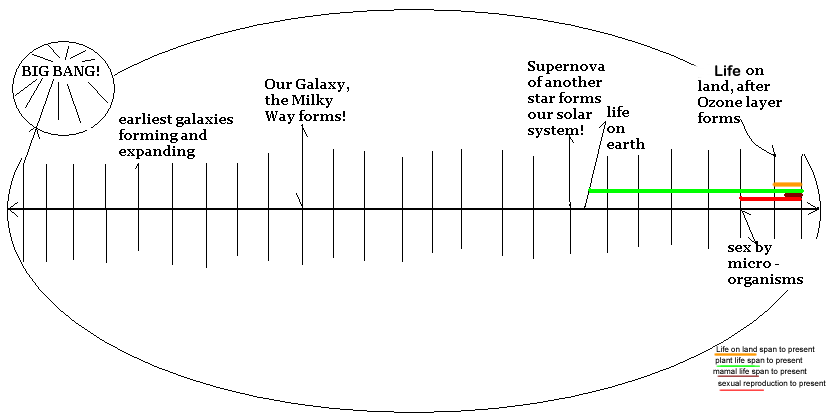
The Astronomy timeline does reveal the earth's history in the context of the rest of the universe, at least as far as we can verify it through science. Our galaxy was formed relatively late compared to other galaxies; our solar system, was formed through a supernova explosion of a larger star. Life on earth formed about 500 million years after and it took roughly 3.5 billion years before the Ozone layer was ready for the “Cambrian Explosion” of land life. Sexual reproduction (the red line) has also been around for a billion years and it predates the Cambrian Explosion on land. The brown line represents mammals and they have only been around since a meteorite eliminated the cold sensitive dinosaurs, the largest of the reptiles.
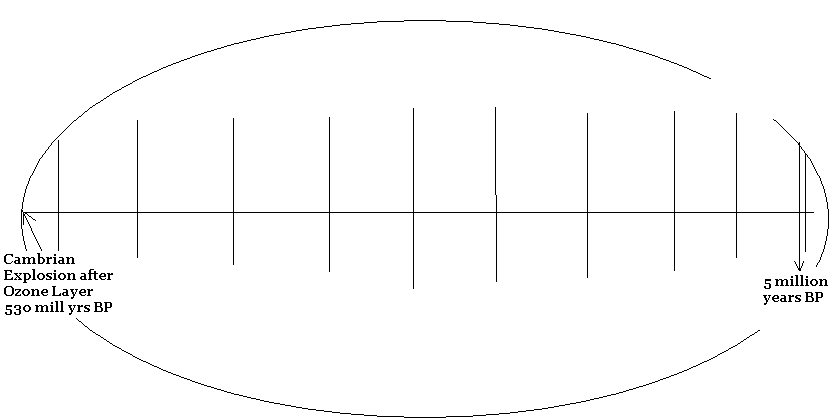
The perspective of Paleontology represents, approximately, half of the last section of the astronomy timeline. What appears to be at issue in the article is whether or not the Cambrian Explosion of life on earth, including humans, makes us any more special than forms of life that predated this period. Since the characteristic of having spinal chords predates the Cambrian Explosion, the author argues, we are “of it and not It.”
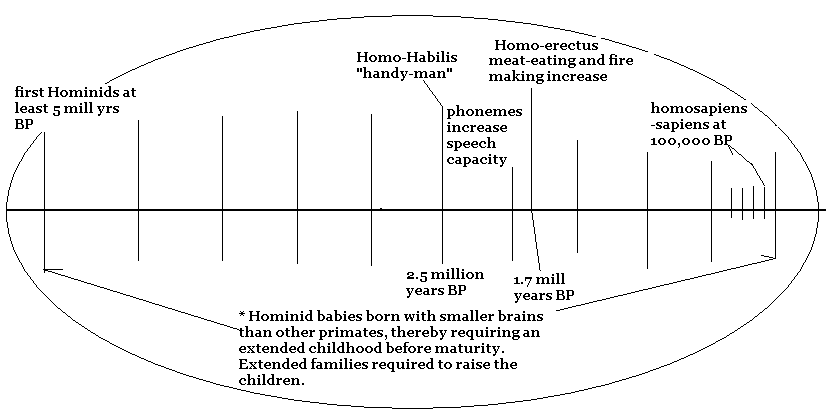
Anthropology timeline represents the section of the paleontology line from 5 million years point. Anthropologists argue about what it is to be human, what is human nature, and how have we populated the earth over time. A key feature that distinguishes us from other primates, according to anthropologists is the extended childhood required to grow our brains and reach maturity for sexual reproduction. Our hominid childhood lasts about twice as long as other primates, our closest relatives, the Chimpanzees and the Bonobos with whom humans share between 97 and 99 percent of the same DNA. For example, we share the gene for balding with the Bonobos. Bonobo society is also interesting in the dominance of females and their methods of conflict resolution which is so much less violent than chimpanzee society. Primatologists and Anthropolgists argue that their scale of viewing human history in the context of other primates calls into question assumtions regarding the "differences" regarding the nature of gender relations in human and primate history. In the larger course of human history (at least 100,000 years) especially during periods before the agricultural revolution, women have often had more status than men. Between 20,000 years ago and 10,000 years ago the first representations of the human form were female; and in many non-agricultural societies today, females often have a higher status than they do in agricultural societies. Because the written record is the primary basis for our study of world history, we do not know the extent of the variation of gender relations in human history, but it does appear that the agricultural revolution set the status of women back from what it was (and is) in non-agricultural societies; and it was not until the industrial revolution in the 19th century that women begin to gain back some of their status and rights.



To science we owe dramatic changes in our smug self-image. Astronomy taught us that our earth isn't the center of the universe but merely one of billions of heavenly bodies. From biology we learned that we weren't specially created by God but evolved along with millions of other species. Now archaeology is demolishing another sacred belief: that human history over the past million years has been a long tale of progress. In particular, recent discoveries suggest that the adoption of agriculture, supposedly our most decisive step toward a better life, was in many ways a catastrophe from which we have never recovered. With agriculture came the gross social and sexual inequality, the disease and despotism, that curse our existence.
At first, the evidence against this revisionist interpretation will strike twentieth century Americans as irrefutable. We're better off in almost every respect than people of the Middle Ages, who in turn had it easier than cavemen, who in turn were better off than apes. Just count our advantages. We enjoy the most abundant and varied foods, the best tools and material goods, some of the longest and healthiest lives, in history. Most of us are safe from starvation and predators. We get our energy from oil and machines, not from our sweat. What neo-Luddite among us would trade his life for that of a medieval peasant, a caveman, or an ape?
For most of our history we supported ourselves by hunting and gathering: we hunted wild animals and foraged for wild plants. It's a life that philosophers have traditionally regarded as nasty, brutish, and short. Since no food is grown and little is stored, there is (in this view) no respite from the struggle that starts anew each day to find wild foods and avoid starving. Our escape from this misery was facilitated only 10,000 years ago, when in different parts of the world people began to domesticate plants and animals. The agricultural revolution spread until today it's nearly universal and few tribes of hunter-gatherers survive.
From the progressivist perspective on which I was brought up, to ask "Why did almost all our hunter-gatherer ancestors adopt agriculture?" is silly. Of course they adopted it because agriculture is an efficient way to get more food for less work. Planted crops yield far more tons per acre than roots and berries. Just imagine a band of savages, exhausted from searching for nuts or chasing wild animals, suddenly grazing for the first time at a fruit-laden orchard or a pasture full of sheep. How many milliseconds do you think it would take them to appreciate the advantages of agriculture?
The progressivist party line sometimes even goes so far as to credit agriculture with the remarkable flowering of art that has taken place over the past few thousand years. Since crops can be stored, and since it takes less time to pick food from a garden than to find it in the wild, agriculture gave us free time that hunter-gatherers never had. Thus it was agriculture that enabled us to build the Parthenon and compose the B-minor Mass.
While the case for the progressivist view seems overwhelming, it's hard to prove. How do you show that the lives of people 10,000 years ago got better when they abandoned hunting and gathering for farming? Until recently, archaeologists had to resort to indirect tests, whose results (surprisingly) failed to support the progressivist view. Here's one example of an indirect test: Are twentieth century hunter-gatherers really worse off than farmers? Scattered throughout the world, several dozen groups of so-called primitive people, like the Kalahari bushmen, continue to support themselves that way. It turns out that these people have plenty of leisure time, sleep a good deal, and work less hard than their farming neighbors. For instance, the average time devoted each week to obtaining food is only 12 to 19 hours for one group of Bushmen, 14 hours or less for the Hadza nomads of Tanzania. One Bushman, when asked why he hadn't emulated neighboring tribes by adopting agriculture, replied, "Why should we, when there are so many mongongo nuts in the world?"
While farmers concentrate on high-carbohydrate crops like rice and potatoes, the mix of wild plants and animals in the diets of surviving hunter-gatherers provides more protein and a bettter balance of other nutrients. In one study, the Bushmen's average daily food intake (during a month when food was plentiful) was 2,140 calories and 93 grams of protein, considerably greater than the recommended daily allowance for people of their size. It's almost inconceivable that Bushmen, who eat 75 or so wild plants, could die of starvation the way hundreds of thousands of Irish farmers and their families did during the potato famine of the 1840s.
So the lives of at least the surviving hunter-gatherers aren't nasty and brutish, even though farmers have pushed them into some of the world's worst real estate. But modern hunter-gatherer societies that have rubbed shoulders with farming societies for thousands of years don't tell us about conditions before the agricultural revolution. The progressivist view is really making a claim about the distant past: that the lives of primitive people improved when they switched from gathering to farming. Archaeologists can date that switch by distinguishing remains of wild plants and animals from those of domesticated ones in prehistoric garbage dumps.
How can one deduce the health of the prehistoric garbage makers, and thereby directly test the progressivist view? That question has become answerable only in recent years, in part through the newly emerging techniques of paleopathology, the study of signs of disease in the remains of ancient peoples.
In some lucky situations, the paleopathologist has almost as much material to study as a pathologist today. For example, archaeologists in the Chilean deserts found well preserved mummies whose medical conditions at time of death could be determined by autopsy (Discover, October 1987). And feces of long-dead Indians who lived in dry caves in Nevada remain sufficiently well preserved to be examined for hookworm and other parasites.
Usually the only human remains available for study are skeletons, but they permit a surprising number of deductions. To begin with, a skeleton reveals its owner's sex, weight, and approximate age. In the few cases where there are many skeletons, one can construct mortality tables like the ones life insurance companies use to calculate expected life span and risk of death at any given age. Paleopathologists can also calculate growth rates by measuring bones of people of different ages, examine teeth for enamel defects (signs of childhood malnutrition), and recognize scars left on bones by anemia, tuberculosis, leprosy, and other diseases.
One straight forward example of what paleopathologists have learned from skeletons concerns historical changes in height. Skeletons from Greece and Turkey show that the average height of hunger-gatherers toward the end of the ice ages was a generous 5' 9" for men, 5' 5" for women. With the adoption of agriculture, height crashed, and by 3000 B. C. had reached a low of only 5' 3" for men, 5' for women. By classical times heights were very slowly on the rise again, but modern Greeks and Turks have still not regained the average height of their distant ancestors.
Another example of paleopathology at work is the study of Indian skeletons from burial mounds in the Illinois and Ohio river valleys. At Dickson Mounds, located near the confluence of the Spoon and Illinois rivers, archaeologists have excavated some 800 skeletons that paint a picture of the health changes that occurred when a hunter-gatherer culture gave way to intensive maize farming around A. D. 1150. Studies by George Armelagos and his colleagues then at the University of Massachusetts show these early farmers paid a price for their new-found livelihood. Compared to the hunter-gatherers who preceded them, the farmers had a nearly 50 per cent increase in enamel defects indicative of malnutrition, a fourfold increase in iron-deficiency anemia (evidenced bya bone condition called porotic hyperostosis), a theefold rise in bone lesions reflecting infectious disease in general, and an increase in degenerative conditions of the spine, probably reflecting a lot of hard physical labor. "Life expectancy at birth in the pre-agricultural community was bout twenty-six years," says Armelagos, "but in the post-agricultural community it was nineteen years. So these episodes of nutritional stress and infectious disease were seriously affecting their ability to survive."
The evidence suggests that the Indians at Dickson Mounds, like many other primitive peoples, took up farming not by choice but from necessity in order to feed their constantly growing numbers. "I don't think most hunger-gatherers farmed until they had to, and when they switched to farming they traded quality for quantity," says Mark Cohen of the State University of New York at Plattsburgh, co-editor with Armelagos, of one of the seminal books in the field, Paleopathology at the Origins of Agriculture . "When I first started making that argument ten years ago, not many people agreed with me. Now it's become a respectable, albeit controversial, side of the debate."
There are at least three sets of reasons to explain the findings that agriculture was bad for health. First, hunter-gatherers enjoyed a varied diet, while early farmers obtained most of their food from one or a few starchy crops. The farmers gained cheap calories at the cost of poor nutrition. (today just three high-carbohydrate plants–wheat, rice, and corn–provide the bulk of the calories consumed by the human species, yet each one is deficient in certain vitamins or amino acids essential to life.) Second, because of dependence on a limited number of crops, farmers ran the risk of starvation if one crop failed. Finally, the mere fact that agriculture encouraged people to clump together in crowded societies, many of which then carried on trade with other crowded societies, led to the spread of parasites and infectious disease. (Some archaeologists think it was the crowding, rather than agriculture, that promoted disease, but this is a chicken-and-egg argument, because crowding encourages agriculture and vice versa.) Epidemics couldn't take hold when populations were scattered in small bands that constantly shifted camp. Tuberculosis and diarrheal disease had to await the rise of farming, measles and bubonic plague the appearnce of large cities.

Besides malnutrition, starvation, and epidemic diseases, farming helped bring another curse upon humanity: deep class divisions. Hunter-gatherers have little or no stored food, and no concentrated food sources, like an orchard or a herd of cows: they live off the wild plants and animals they obtain each day. Therefore, there can be no kings, no class of social parasites who grow fat on food seized from others. Only in a farming population could a healthy, non-producing élite set itself above the disease-ridden masses. Skeletons from Greek tombs at Mycenae c. 1500 B. C. suggest that royals enjoyed a better diet than commoners, since the royal skeletons were two or three inches taller and had better teeth (on the average, one instead of six cavities or missing teeth). Among Chilean mummies from c. A. D. 1000, the élite were distinguished not only by ornaments and gold hair clips but also by a fourfold lower rate of bone lesions caused by disease.
Similar contrasts in nutrition and health persist on a global scale today. To people in rich countries like the U. S., it sounds ridiculous to extol the virtues of hunting and gathering. But Americans are an élite, dependent on oil and minerals that must often be imported from countries with poorer health and nutrition. If one could choose between being a peasant farmer in Ethiopia or a bushman gatherer in the Kalahari, which do you think would be the better choice?
Farming may have encouraged inequality between the sexes, as well. Freed from the need to transport their babies during a nomadic existence, and under pressure to produce more hands to till the fields, farming women tended to have more frequent pregnancies than their hunter-gatherer counterparts–with consequent drains on their health. Among the Chilean mummies for example, more women than men had bone lesions from infectious disease.
Women in agricultural societies were sometimes made beasts of burden. In New Guinea farming communities today I often see women staggering under loads of vegetables and firewood while the men walk empty-handed. Once while on a field trip there studying birds, I offered to pay some villagers to carry supplies from an airstrip to my mountain camp. The heaviest item was a 110-pound bag of rice, which I lashed to a pole and assigned to a team of four men to shoulder together. When I eventually caught up with the villagers, the men were carrying light loads, while one small woman weighing less than the bag of rice was bent under it, supporting its weight by a cord across her temples.
As for the claim that agriculture encouraged the flowering of art by providing us with leisure time, modern hunter-gatherers have at least as much free time as do farmers. The whole emphasis on leisure time as a critical factor seems to me misguided. Gorillas have had ample free time to build their own Parthenon, had they wanted to. While post-agricultural technological advances did make new art forms possible and preservation of art easier, great paintings and sculptures were already being produced by hunter-gatherers 15,000 years ago, and were still being produced as recently as the last century by such hunter-gatherers as some Eskimos and the Indians of the Pacific Northwest.
 Thus with the advent of agriculture and élite became better off, but most people became wors e off. Instead of swallowing the progressivist party line that we chose agriculture because it was good for us, we must ask how we got trapped by it despite its pitfalls.
Thus with the advent of agriculture and élite became better off, but most people became wors e off. Instead of swallowing the progressivist party line that we chose agriculture because it was good for us, we must ask how we got trapped by it despite its pitfalls.
One answer boils down to the adage "Might makes right." Farming could support many more people than hunting, albeit with a poorer quality of life. (Population densities of hunter-gatherers are rarely over on eperson per ten square miles, while farmers average 100 times that.) Partly, this is because a field planted entirely in edible crops lets one feed far more mouths than a forest with scattered edible plants. Partly, too, it's because nomadic hunter-gatherers have to keep their children spaced at four-year intervals by infanticide and other means, since a mother must carry her toddler until it's old enough to keep up with the adults. Because farm women don't have that burden, they can and often do bear a child every two years.
As population densities of hunter-gatherers slowly rose at the end of the ice ages, bands had to choose between feeding more mouths by taking the first steps toward agriculture, or else finding ways to limit growth. Some bands chose the former solution, unable to anticipate the evils of farming, and seduced by the transient abundance they enjoyed until population growth caught up with increased food production. Such bands outbred and then drove off or killed the bands that chose to remain hunter-gatherers, because a hundred malnourished farmers can still outfight one healthy hunter. It's not that hunter-gatherers abandonded their life style, but that those sensible enough not to abandon it were forced out of all areas except the ones farmers didn't want.
At this point it's instructive to recall the common complaint that archaeology is a luxury, concerned with the remote past, and offering no lessons for the present. Archaeologists studying the rise of farming have reconstructed a crucial stage at which we made the worst mistake in human history. Forced to choose between limiting population or trying to increase food production, we chose the latter and ended up with starvation, warfare, and tyranny.
Hunter-gatherers practiced the most successful and longest-lasting life style in human history. In contrast, we're still struggling with the mess into which agriculture has tumbled us, and it's unclear whether we can solve it. Suppose that an archaeologist who had visited from outer space were trying to explain human history to his fellow spacelings. He might illustrate the results of his digs by a 24-hour clock on which one hour represents 100,000 years of real past time. If the history of the human race began at midnight, then we would now be almost at the end of our first day. We lived as hunter-gatherers for nearly the whole of that day, from midnight through dawn, noon, and sunset. Finally, at 11:54 p. m. we adopted agriculture. As our second midnight approaches, will the plight of famine-stricken peasants gradually spread to engulf us all? Or will we somehow achieve those seductive blessings that we imagine behind agriculture's glittering façade, and that have so far eluded us?